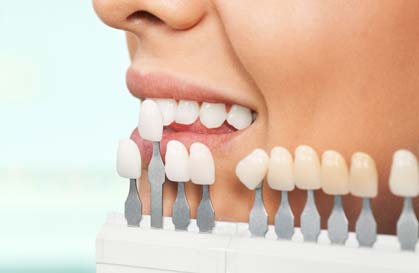
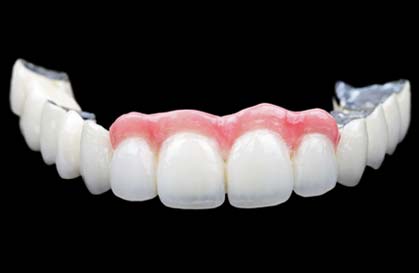
Thus, removable restorations include full dentures and partial dentures, while fixed restorations include crowns, bridges and veneers.
Finally, prosthodontics deals also with removable or fixed restorations supported on implants.
Interestingly, full dentures can also improve the overall esthetics of the face in patients that have lost all their teeth. Specifically, after the loss of natural teeth the lip and cheeks are left largely unsupported. Thus, the mouth “shrinks” and wrinkles appear altering the physical characteristics of the person. But this is reversed with dentures. Hence, the dentures restore not only mastication and vocalization but the overall facial aesthetics.
Dentures must be removed from the mouth for some time during the night in order to be cleaned and to allow the soft tissues (gums) to “rest”.
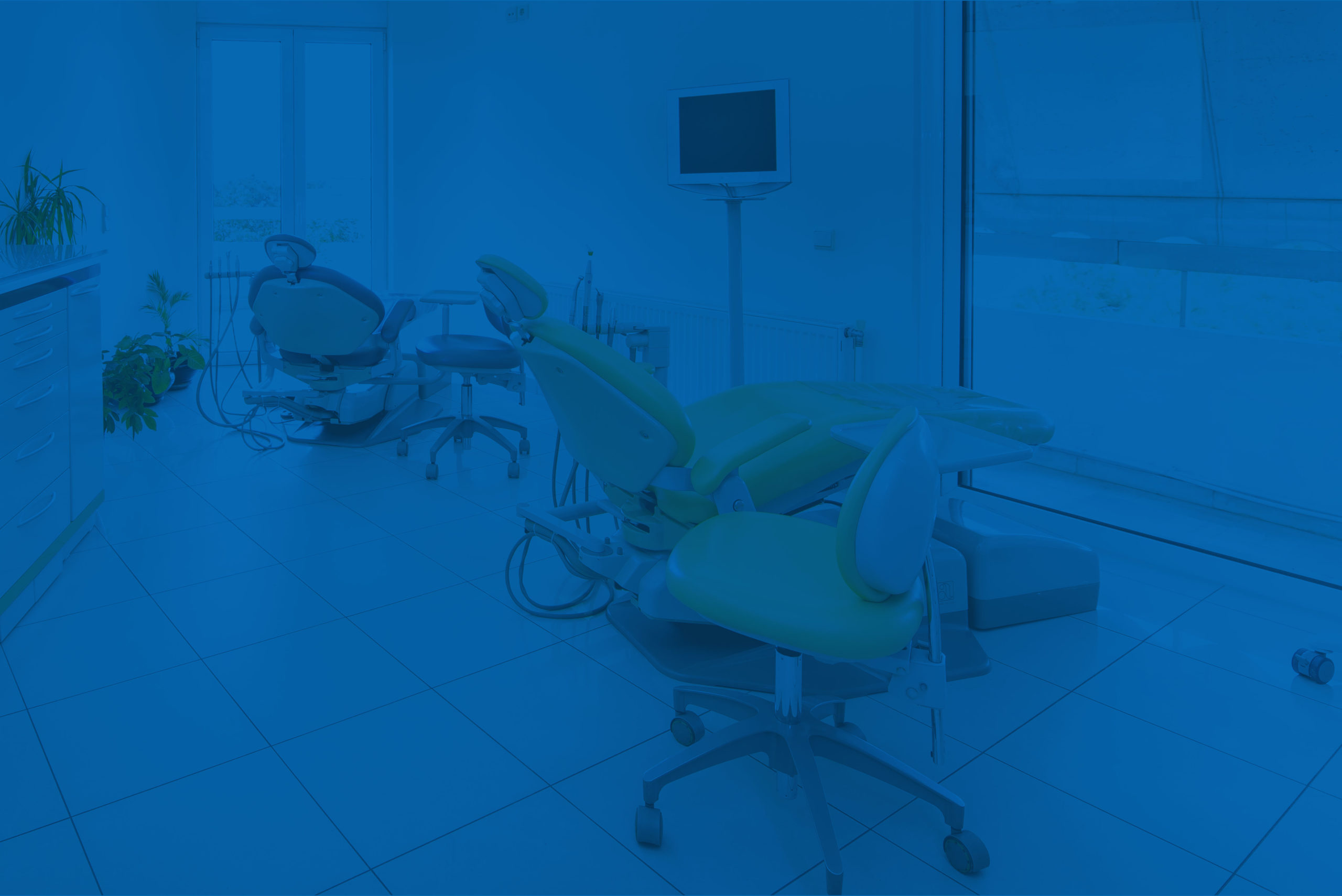
Partial dentures must be removed from the mouth for some time during the night in order to be cleaned and to allow the soft tissues (gums) to “rest”.
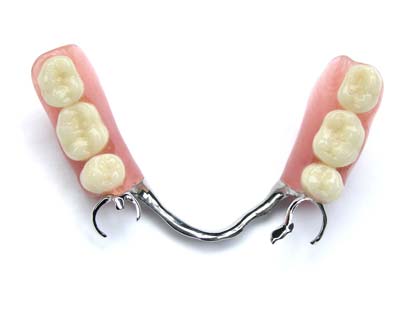
Due to the attachment of the over-denture to the implants the denture does not need to fit firmly to the gums and hence the over-dentures leave the roof of the mouth (palate) uncovered. Thus, implants, besides increasing the support of the denture, allow, also, the fabrication of smaller dentures which are more tolerable by the patients.
However, implant supported dentures must be removed from the mouth for some time during the night in order to be cleaned and to allow the soft tissues (gums) to “rest”.
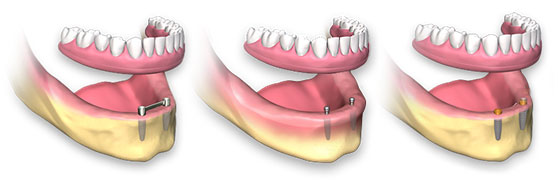
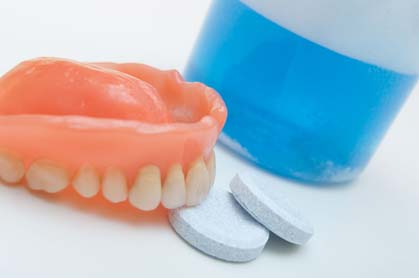
Food that gets trapped on the dentures can be easily removed by rinsing with water. However, since, dentures have a solid surface on which various bacteria may colonize the patient needs to brush them with a toothbrush and liquid soap on a daily basis. Additionally, the patient can use some antimicrobial tablets that help eliminate the bacteria that grow on the dentures. For proper use of these tablets it is advisable to follow the manufacturer’s instructions. By having the dentures clean the patient minimizes the risk for gum irritation and fungal infection.
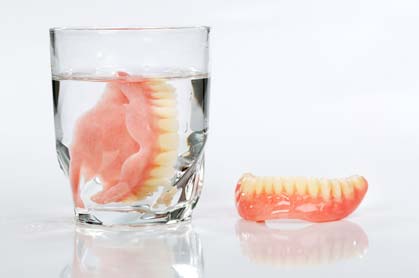
Also, because the dentures are made of acrylic when they are outside the mouth they should be kept in a container with water to prevent them from drying out.
- Antimicrobial tablets for denture cleaning
- Dentures in water
Finally, patients with dogs, should know that their pets love chewing dentures, so these patients should be particularly careful where they leave their dentures when they remove them from their mouths.
Why do dentures get loose over time?
There are three main reasons that can cause loosening of the dentures:
- After many times of placing and removing the partial denture from the mouth, the clasps that retain the denture in place may get loose and may not attach precisely on the remaining teeth. In this case, the dentist can adjust the clasps to achieve proper fit.
- Over time, physiologically, jaw bone resorption may occur in areas where teeth have been lost. Thus the morphology of the gums under the denture changes. Once this happens the denture loses its precise fit with the gums and retention is compromised. To address this problem, patients can enhance retention by using special adhesives for dentures (eg Correga) which stick the denture with the soft tissues (gums). This solution, of course, although very common, does not solve the cause of the problem. Ideally, the patient should have a new denture made that will fit properly according to the new anatomy of the area. Alternatively, the dentist can fill up the old denture with acrylic to compensate for the void created by bone resorption. This process is called denture reline.

- In some cases jaw bone resorption may be so extensive that the remaining surface of the gums is insufficient to support the denture. In these cases a denture supported by dental implants may be the only solution to increase retention.
How can the retention of a denture increase?
See previous question.
Is there a way to make the clasps of a partial denture invisible?
The clasps of a partial dentures are made of metal and are often visible when the patient talks or laughs. To address this esthetic concern the clasps can be coated with white ceramic to blend better with the remaining natural teeth. Also, in some cases where crowns are going to be placed on the remaining natural teeth the partial denture may be fabricated without clasps. In order to achieve retention these dentures and crowns have internal precision attachments that are practically invisible.
Can a broken denture be repaired?
If you break your denture the dentist can, most likely, fix it without having to fabricate a new one. The dentist will take an impression and will keep your denture for a day or two. Similarly, if a denture-tooth is broken then the dentist can adjust a new tooth on the denture.
If I have a partial denture and extract a natural tooth do I need to make a new denture?
It depends on what tooth is extracted. If that tooth played a key role in retaining the partial denture, then most likely, a new denture needs to be fabricated. However, if the tooth that was lost was not involved in the support of the denture, then most of the times, a new denture tooth can be adjusted on the old denture and replace the missing tooth.
Will I get used to my new denture?
It is obvious that dentures are relatively bulky foreign objects that are placed in the patient’s mouth. Hence, it is important that the patient is not negatively predisposed to the fact that he will wear dentures. There are many cases where the dentures fit perfectly and have excellent retention however the patient does not get used to them due to psychological reasons. Since the denture is a foreign body the patient needs to allow some time to get used to it. Yet, the patient must immediately indicate a sore spot since the dentist may adjust the denture and relieve the patient from any discomfort.
Finally, in some cases jaw bone resorption may be so extensive that the remaining surface of the gums is insufficient to support the denture. In these cases a denture supported by dental implants may be the only solution to increase retention. The dentist however through a thorough clinical examination may predict this unpleasant situation and promptly inform the patient about this treatment option.
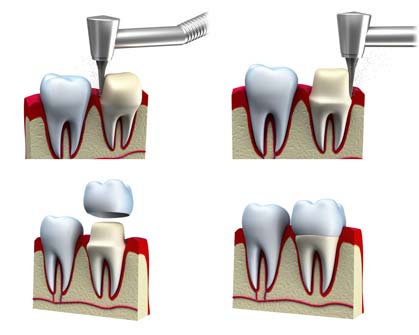
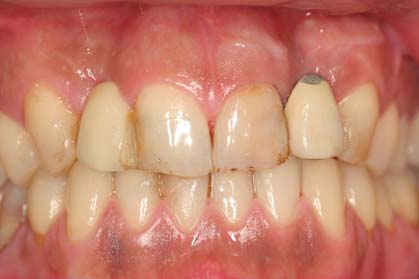
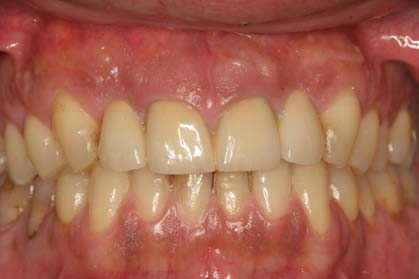
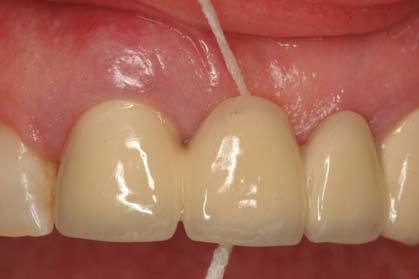
The crown may have internally a metal framework which is coated externally with ceramic (metal-ceramic crown) or may be entirely of porcelain (all-ceramic crown). Similar materials are used for the fabrication of crowns supported by dental implants.

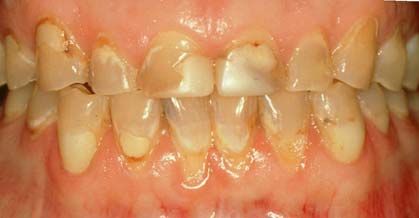
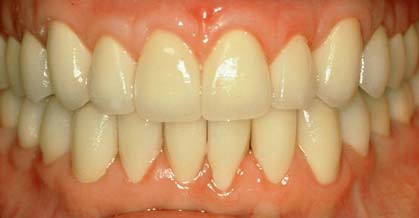
Today the advances in the technology of ceramics allow for the construction of impressive crowns. The great strength of the ceramics used along with the broad selection in shades can lead to an outcome that satisfies even the most aesthetically demanding patient.
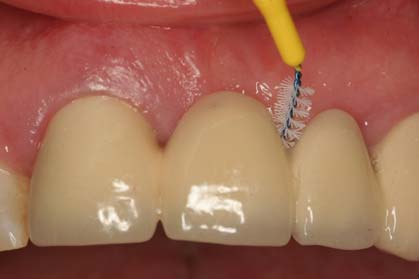
However, it is important that the patient acknowledges that the crown placed on a tooth does not protect it against periodontal disease or root decay. Therefore, after the placement of the crown, the patient must follow all instructions of oral hygiene (toothbrush, floss) as with the remaining natural teeth.
Finally, it should be noted that in some cases the destruction of the tooth is so extensive that the remaining tooth structure is not sufficient to hold the crown. In these cases a metal post and core may be necessary to be fabricated first. However, since this post and core enters the root of the tooth a root canal treatment will also be performed.
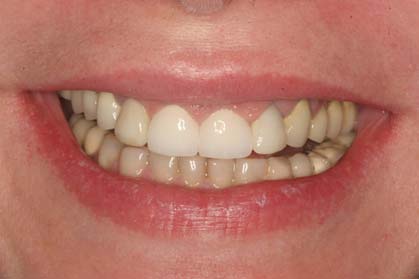
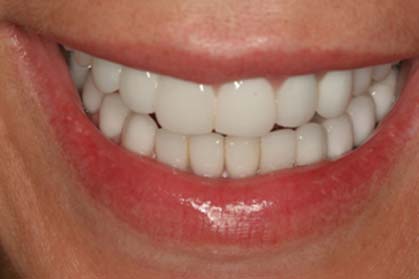
- Before
- After full-mouth rehabilitation with all-ceramic crowns
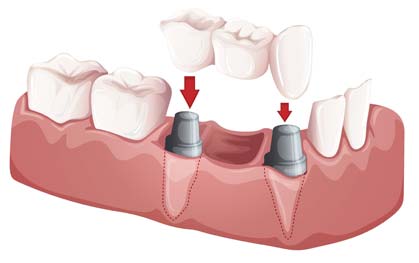
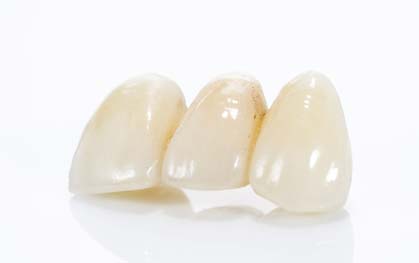
- Metal-ceramic bridge
- All-ceramic bridge
Today the advances in the technology of ceramics allow for the construction of impressive bridges. The great strength of the ceramics used along with the broad selection in shades can lead to an outcome that satisfies even the most aesthetically demanding patient.
- Selection of the precise shade of a bridge to match the natural teeth
- Bridge with pink porcelain
Case 1
- Before
- After full-mouth reconstruction with all-ceramic bridges and crowns
Case 2
- Before
- After metal-ceramic bridge at the four anterior upper teeth
However, despite the increased strength of the porcelain, when extensive bridges are constructed or when the patient grinds his teeth (bruxism), an acrylic transparent bite-guard is fabricated in order to protect the porcelain from micro-fractures.
It is also important, that the patient acknowledges that the bridges do not protect the teeth against periodontal disease or root decay. Therefore, after the placement of a bridge, the patient must follow all instructions of oral hygiene (toothbrush, super-floss inter-dental brushes) as with the remaining natural teeth.
- Use of super-floss under a bridge
- Cleaning of a bridge with inter-dental brushes
Finally, it should be noted that in some cases the destruction of the supporting teeth is so extensive that the remaining tooth structure is not sufficient to hold the bridge. In these cases a metal post and core may be necessary to be fabricated first. However, since this post and core enters the root of the tooth a root canal treatment will also be performed.
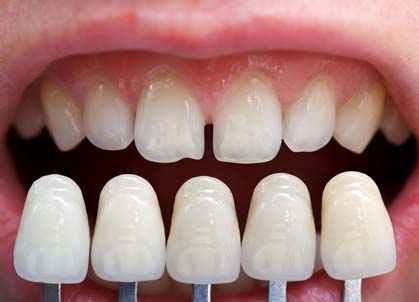
Today the advances in the technology of ceramics and composite resins allow for the construction of impressive veneers. The great strength of these materials along with the broad selection in shades can lead to an outcome that satisfies even the most aesthetically demanding patient.
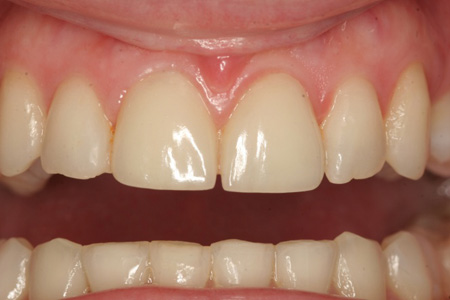
Thus teeth with small fractures, or uneven shape, or with discoloration may benefit from veneers. In addition, by placing veneers on adjacent teeth can improve the overall smile of the patient. Black triangles between teeth can close, the shape of the teeth can improve and become more symmetric, while discolorations between teeth can be eliminated.
Should I choose all-ceramic or metal-ceramic crowns / bridges?
Both options may have an excellent esthetic result. Nevertheless, the metal framework of metal-ceramic restorations prevents the diffusion of the light through the transparent porcelain. Hence, all-ceramic restorations are considered to outbalance metal-ceramic restorations esthetically. On the other hand, in all-ceramic restorations, the lack of metal framework renders the ceramic thicker and more “unsupported” which increases the risk for micro-fractures. Therefore, a general rule, is to place all-ceramic restorations in front teeth where esthetics are very important and metal-ceramic restorations at the posterior teeth where strength is more important.
Should I make a bridge or have an implant placed?
The answer to this question is not always easy and depends on the case. If the adjacent natural teeth that will support the bridge are intact then it is better to place an implant to avoid grinding down the teeth. In addition, oral hygiene is easier around an implant rather than around a bridge. Thus, despite the higher initial cost of the implant in the long run this treatment may prove to be a more profitable investment. On the other hand, if the adjacent teeth need to be restored with crowns and are strong enough to support the bridge then the option of placing a bridge may also be good.
Until the final crown/bridge is placed what goes on prepared teeth?
A prepared (grinded down) tooth should never be left uncovered for the following reasons:
1) the prepared tooth is exposed to various stimuli and is more vulnerable to pain and pulp damage,
2) the prepared tooth is more prone to decay,
3) the prepared tooth is weak and can break while chewing,
4) the prepared tooth negatively affects mastication and occlusion,
5) the prepared tooth can trap food and prevent proper oral hygiene and
6) the prepared tooth can cause esthetic problems, especially if it is a front tooth.
For all these reasons, after preparing a tooth, an interim (temporary) acrylic restoration is made. This temporary restoration resembles in shape and color the final restoration.
Do I have to have a root canal at teeth that will receive a crown or a bridge?
Root canal treatment is not mandatory every time a tooth is going to be grinded down to receive a crown/bridge. However, many dentists proceed preemptively with a root canal therapy in order to minimize the risk for root sensitivity or damage of the pulp after tooth preparation.