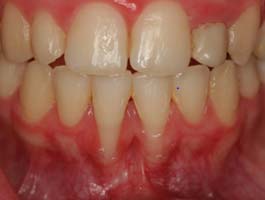
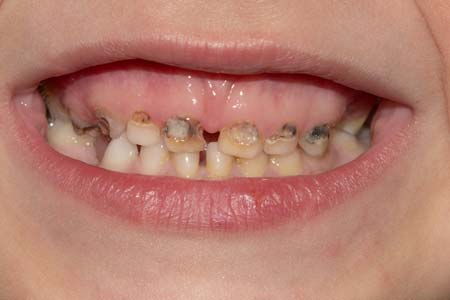
The gums and the enamel provide protection to the teeth. When the enamel is destroyed or the gums have receded, the porous dentine is left exposed, resulting in the increased risk of developing tooth sensitivity. This sensitivity usually leads to an acute and a penetrating pain feeling, when the patient consumes hot or cold drinks or sweet and sour foods or just with simple contact. Pain can even occur while breathing fresh air. When the problem lies in the neck of the tooth, where the crown of the tooth connects with the root of the tooth, the condition is called cervical tooth sensitivity.

Tooth sensitivity is a serious condition of the mouth that needs to be treated, since it may lead to other unpleasant problems. People suffering from tooth sensitivity usually neglect practicing oral hygiene in order to avoid pain. Thus teeth become more vulnerable to caries and periodontal disease.
- periodontal disease may cause the gums to recede and thus expose the root surface.
- wrong way of brushing, that leads to the abrasion of the tooth enamel and exposure of the porous dentine.
- teeth grinding (bruxism), that causes the damage of the enamel and the exposure of the porous dentine.
- acidic foods and drinks consumption, that corrode the enamel of teeth and expose the porous dentine.
- dental caries, that destroys the enamel of the teeth, exposing the porous dentine.
- teeth trauma (cracking, fracture), that reaches deep in the dentine, communicating external stimuli to the nerves of the teeth.
- teeth whitening, when the guidelines are not followed.
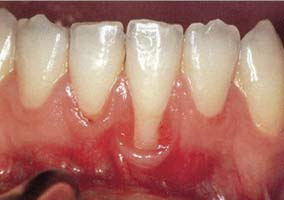
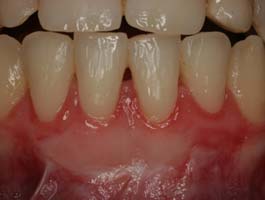
- Tooth root exposure due to poor oral hygiene
- Teeth root exposure due to intense brushing with a hard toothbrush
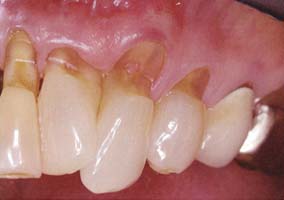
- Pulp exposure due to fractured tooth
If you have tooth sensitivity you should tell your dentist at Dental Group. After the diagnosis of the exact cause of the sensitivity, he will inform you about the treatment options.
Tooth sensitivity is treated with various methods. Depending on the severity of the problem the following actions could be proposed:
- Use of a desensitizing toothpaste. The desirable improvement is usually achieved after the use of this type of toothpaste for several weeks. However, this treatment is not successful for all patients.
- Fluoridation. Fluoride gels or lacquers are used locally by the dentist or the pediatric dentist, so as to close the dentine tubular leads and isolate the nerves of a tooth from external stimuli.

- Teeth polishing, through the use of a desensitizing polishing paste.
- Resin veneers. They are used to cover the pores of the dentine.
- Dental crowns. They are used as a treatment option in order to cover the exposed root surface.
- Root covering with gum graft.
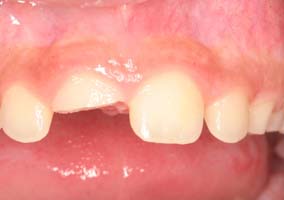
- Before root coverage
- After root coverage with a gum graft
- Intended endodontic treatment (root canal treatment), when all other measures of treatment have failed and tooth sensitivity affects the patient’s quality of life.
- thorough oral hygiene practice
- correct brushing technique of the teeth
- use of soft or medium hardness toothbrush
- reduction of acidic foods and beverages consumption
- teeth whitening, according to the dentist’s guidelines
According to studies, 50% of the population experiences this unpleasant condition. Huge amounts of money are spent to find cures for bad breath such as mouthwashes, gums, caramels, etc.
For the effective treatment the correct diagnosis is necessary because many times halitosis is just in the mind of the patient (pseudohalitosis).

Exogenous factors
- smoking
- alcohol
- various foods (garlic, onion, etc.)
- bad nutrition (diet)
- Bad breath due to periodontitis
Endogenous factors
- gingivitis and periodontitis
- tongue coating with bacteria
- caries
- abscesses
- food impaction
- poor cleaning of dentures
- poor oral hygiene
- dry mouth due to reduced saliva flow
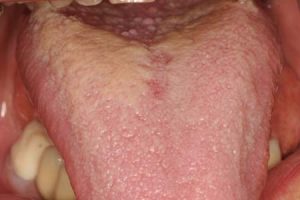
- Coated tongue
90% of the endogenous factors originated from the oral cavity, while the rest are associated to conditions outside the mouth, such as:
- systemic diseases (liver cirrhosis, renal failure, etc.)
- tonsillitis, bronchitis
- gastro-oesophageal reflux
- metabolic disorders
For the treatment of bad breath that originates from oral bacteria, the therapy depends on the reduction of the bacterial load in the mouth and particularly from the tongue. Specifically, for the treatment of the bad breath the following actions are generally recommended:
- treatment of gingivitis and periodontitis
- treatment of carious lesions
- emphasis on the cleaning of the tongue
- correct oral hygiene practice
- oral and pharynx washes through the use of a mouthwash
- use of special tablets that bind the odors that cause bad breath
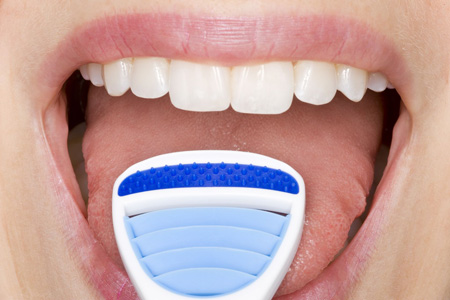
The tongue can often be the main source of smelly odors. This is the reason why so much importance is laid on its cleaning through the use of special toothbrushes or scrapers. People with large grooves on the tongue are prone to develop halitosis.
The saliva is a transparent and lightly sticky liquid, that is excreted form the salivary glands in the mouth. Its main function is to facilitate the swallowing process of foods and the process of digestion. Additionally, the saliva maintains the moisture of the mouth stable, rinses the food residues from the teeth, neutralizes acids and conveys antibodies against the threat of bacteria, hence, protecting from caries and gingivitis. Finally, it contributes tremendously in the sense of taste.
When not enough amount of saliva is produced, the mouth gets dry and an unpleasant sensation appears. This is called xerostomia. In severe cases, xerostomia leads to oral and throat malfunctions, and it can also affect negatively the quality of life. Unfortunately, there is no way to prevent xerostomia. However, there are several ways to treat it.
Dry mouth affects approximately 10% of the general population. It is more common to women than men, and is a characteristic symptom of elderly people and people who often take various medications. Finally, xerostomia is one of the main symptoms of individuals who suffer from Sjögren syndrome.
- discomfort during speech and swallowing
- discomfort during eating
- difficulty to taste
- constant cough
- dried and chapped lips
- tongue and throat burn
- white tongue (candidiasis)
- ulcers and irritations of the soft tissues of the mouth
- periodontitis

The main causes are:
- side effects of various medications such as antidepressants, antihistamines, antiallergic substances, diuretics, etc.
- symptoms of systemic diseases such as HIV, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
- side effects of treatment procedures, such as radiation therapy, chemotherapy
- blocking of a salivary porous
- stress, agony, oppression
- dehydration
- characteristic symptom of Sjogren syndrome
The following actions promote the production of saliva:
- low sugars and carbs diet
- consumption of snacks restriction
- reduction of acidic and sour foods consumption
- large quantity consumption of water, particularly during meals
- slow chewing of food
- brushing of teeth using a fluoride toothpaste
- use of a fluoride mouthwash
- no sugar gum chewing
- cherry or olive pit sucking
- breathing through the nose
- use of moisturizer in the room
Exogenous tooth corrosion
- Regular consumption of acidic foods and beverages. It is the most common cause of tooth corrosion. Teeth are at risk every time we consume foods or beverages that create a very acidic environment in the mouth (pH<5,5). Such foods are fruits, natural juices, beverages, even the diet ones, carbonated drinks and generally all sour or sugary foods.
- Acidic medication. They are particularly dangerous when they remain in the mouth for a long time before swallowing.
- The chlorine contained in pool’s water. The risk of teeth corrosion increases proportionally to the frequency of exposure to the chlorine of water during swimming.
Engogenous teeth corrosion
- Gastro-oeshophageal reflux. The acidic fluids of the stomach due to the reflux, come in contact with the teeth resulting in corrosion of the external surface of the teeth.
- Nutritional disorders. Due to the occurrence of regular vomits (anorexia nervosa) and the large consumption of acidic foods (bulimia), anorexic and bulimic individuals develop more regularly than average corrosion of the enamel of their teeth.
The corrosion of the teeth causes the destruction of the enamel of the teeth. Initially, the thickness of the enamel of the teeth is decreased in dimensions, and in the process it gets completely destroyed. Tooth corrosion causes many symptoms which should alarm the patient. Such symptoms are:
- Tooth sensitivity. Due to the destruction of the tooth enamel, tooth sensitivity may occur especially when consuming something hot or cold, sweet or sour, or even when breathing air.
- Tooth decolorization. This happens due to the gradual destruction of the enamel and the exposure of the dentine, which is of yellow color, thus the teeth appear yellowish.
- Tooth transparency. The reduction of the thickness of the teeth due to corrosion has an effect on their transparency. In the case of advanced corrosion, the teeth and especially the front ones have a similar appearance to glass.
- Shape and size modification. The corroded teeth appear small, thin and with an irregular shape due to loss of the dentine substance.
The following actions are proposed as prevention measures for tooth corrosion:
- Reduce the consumption of acidic foods and beverages. It is advisable to consume them, if possible, during meals.
- Drink, if possible, acidic beverages with the use of a drinking straw.
- Eliminate the consumption of carbonated beverages.
- Eat as snacks, foods that are not acidic.
- Choose to drink beverages without sugar.
- Do not brush your teeth immediately after the consumption of acidic foods or drinks or outbreaks of reflux, because the acids temporarily soften the enamel of the teeth, resulting in a bigger risk of the teeth to undergo corrosion.
- Rinse your teeth with water right after the consumption of such foods or drinks.
- Finish your meal with foods that contain calcium, as cheese, for the neutralization of acids.
- Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft toothbrush and use a fluoride toothpaste.
- Chew gums without sugar for the increase of saliva flow.
- Check the causes of regular vomit incidents.
- Visit the dentist’s office regularly for dental examination. The symptoms of corrosion are not easily detected.
- Follow a fluoridation program in the dental office, if necessary.
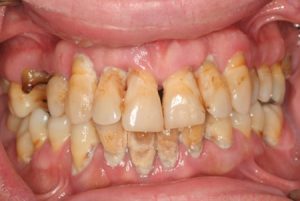
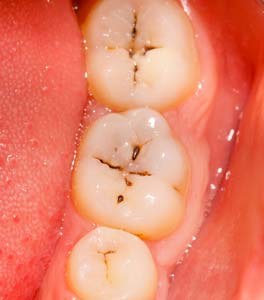
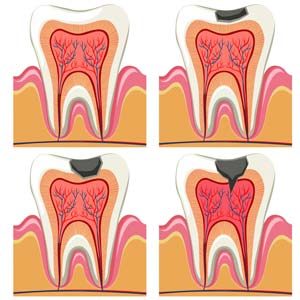
Caries affect the teeth of patients of all ages, even of infants. Nowadays, it is considered an international epidemic. Significantly disturbing are recent data regarding the occurrence of caries in the Greek population. If not treated on time, it can cause pain or inflammation, and even lead to the loss of a tooth. Initially, caries attack the outer surface of a tooth, the enamel, and proceed with affecting the dentine and the pulp, in other words the internal part of the tooth.
- Caries infected teeth of a child
- Caries infected back teeth
Caries can be prevented through correct oral hygiene practice and regular dental examinations.
When the patient consumes foods rich in sugars and starch, bacteria metabolize the sugars into acids. These acids corrode the enamel of the teeth leading to small holes on the surface of the enamel. Then, bacteria and acids can reach deeper in the tooth to the dentine, which is softer and less resistant to such acids, and finally affect the pulp of the tooth where the nerves are located.
Due to the destruction of the external layer of the tooth, the tooth becomes more sensitive to various stimuli (cold or hot) and may even cause toothache. Eventually, if caries infect the pulp of the tooth then the nerve of the tooth dies.
- Poor oral hygiene. In order for caries to develop, the presence of bacteria that metabolize sugars and starch into acids is mandatory. Hence, if bacteria are not removed from the teeth, then there is a high risk of developing caries.
- Foods and beverages than contain sugars and starch. These compounds are responsible for the production of acids in the oral cavity and facilitate the development of caries.
- Fluoride deficits. Fluoride protects the teeth from caries and this is the reason it is artificially added in the water supply systems. Furthermore, fluoride is a component of many toothpastes and mouthwashes. For additional intake of fluoride, the dentist’s recommendation is mandatory.
- Xerostomia. It is induced by the reduced production of saliva. Saliva removes the food residues and the bacterial plaque functioning as an impediment to the development of teeth caries. Additionally, compounds found in the saliva neutralize the acids produced by the oral bacteria.
- Ill-fitting fillings. When they don’t properly fit on the tooth, they obstruct the correct cleaning resulting in the development of caries.
- Eating disorders. Anorexia or bulimia lead to corrosion of the teeth and to the development of caries. The acids produced by the stomach destroy the enamel of the teeth due to regular vomit incidents. Moreover, eating disorders affect the production of saliva as well.
- Radiotherapy and chemotherapy. These can reduce the production of saliva and the ability to protect from caries.
- Fluoridation. Fluoride helps the teeth to restore the damage caused by caries in its early stages of infection. The procedure is performed by the dentist. Fluoride can be in a liquid, gel, foam or polish form. The treatment usually lasts a few minutes.
- Fillings. This is the main treatment option when the carious lesions have progressed and have created a hole in the tooth. The lesion is removed from the tooth and restored with a filling element.
- Dental crowns. When the damage of the tooth is extensive and not enough dental substance exists to support the filling, then the dentist will construct a dental crown.
- Endodontic treatment (root canal procedure). When the bacteria of caries have reached the pulp of the tooth, the nerve of the tooth dies and the endodontic treatment is mandatory.
- Tooth extraction. When the damage of the tooth due to caries is extremely extensive to a point that the tooth cannot be restored, the dentist proceeds to its extraction.
- effective oral hygiene
- periodic fluoridation at the dental clinic
- use of fluoride toothpaste or mouthwash
- balanced and low-sugar and low-starch diet
- regular re-examinations
Who is prone to develop caries?
Teeth can develop caries at all ages. While many believe that children and teenagers are more prone to develop caries, the fact is that caries is an issue of all ages. Even infants can develop caries.
Younger people, possibly, are more vulnerable to caries due to the fact that dentin of younger individuals is less mature and can be more easily destroyed by acids. Older individuals are under a higher risk of developing caries due to gum recession and exposure of the roots. Furthermore, some kind of medicines, like antihypertensives, antihistamines, diuretics or antidepressants cause dry mouth that is related to the development of caries. Additionally, some types of diseases like diabetes, respiratory diseases and oncological treatments are associated to caries progression. Finally, the absence or even the inefficient oral hygiene and the high sugars diet are factors that determine the frequency of carious lesions.
What is nursing bottle's caries?
Nursing’s bottle caries disease is the type of caries that occurs at the infant’s teeth due to prolonged exposure to liquids that contain sugar such as milk, breast milk, juices and all sugary beverages in general. This prolonged exposure is caused by nursing bottles. The caries of the deciduous teeth can cause pain and damage the integrity of permanent teeth that are about to emerge.

Why do the back teeth develop caries more easily?
The chewing surfaces of the back teeth have an irregular surface because they have grooves. Thus, the cleaning of those surfaces through the use of a toothbrush is hard, hence, the food residues and the bacteria get trapped and remain there for a prolonged period of time than desired.

This habit is usually caused by stress and can have unpleasant consequences for the patient. Thus, the continuous and intense friction between the teeth surfaces can cause large scale abrasion. Apart from the aesthetic problem that is induced by the short teeth’s appearance, the destruction of parts of the tooth can make them more sensitive to various stimuli and affect occlusion. Finally, other common symptoms are pain at the chewing muscles, headaches and the improper function of the jaw joint.
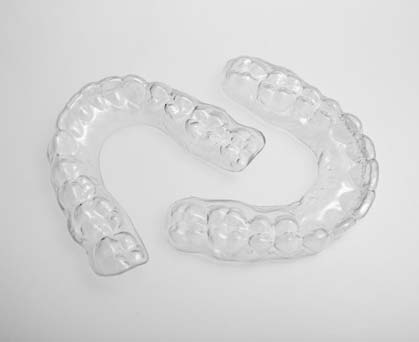
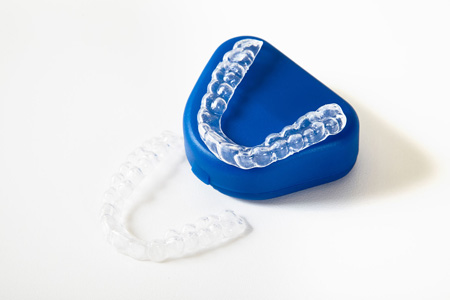
Consequently, if you have noticed that you grind your teeth, you should immediately visit your dentist. For the treatment of this problem, a special individualized transparent bite guard is fabricated and placed on the teeth of the upper or lower jaw. The patient wears the bite guard during bedtime or even when he/she grinds his/her teeth during daytime. The bite guard is made of acrylic material and is much softer than the enamel of the teeth. Thus, the bite guard is the one that gets grinded down and the teeth are protected. Additionally, the bite guard relaxes the chewing muscles and thus headaches and TMJ problems are avoided.
There are three types of protective athletic bite guards:
- Prefabricated bite guard – They are cheap and are available in a prefabricated form, ready to wear without the ability of any adjustment. For this reason, they don’t have a proper fit and thus may cause breathing problems. Consequently, this type of bite guard is not very popular.
- Partially adjustable bite guard – This kind of bite guard is the one that someone can buy from athletic stores. Due to the fact that they are made of thermoplastic materials, the patient can soften the bite guard in hot water and adjust it in his/her mouth. As soon as the bite guard cools down, it gets permanently its final form. They offer a better fit cause they are more individualized. Nevertheless, partially adjustable bite guard are not considered to offer a perfect fit and protection in cases of trauma.
- Fully adjustable bite guard – They are the type of bite guards that are constructed at the dental office and are totally custom made. The dentist gets an impression of the teeth and fabricates the bite guard at the lab. This offers a perfect fit. The bite guard is made of a hypo-allergic and high resistance material, thus offering the maximum possible protection.